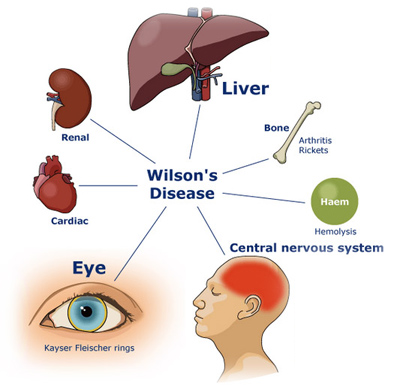
Wilson’s disease is a genetic illness where copper accumulates in the human body. Symptoms are generally linked to the brain and liver. Liver related ailments include nausea, fatigue, fluid build up in the gut, swelling of the legs, yellow skin, and itchiness. Brain associated ailments comprise tremors, muscular stiffness, difficulty talking, personality changes, stress, and hearing or seeing things that others don’t.
Wilson’s disease is an autosomal recessive condition due to a mutation in the Wilson disease protein (ATP7B) gene. For a individual to be influenced they need to inherit a affected replica of this gene from each parent. Diagnosis may be difficult and frequently entails a combination of blood tests, urine tests, and also a liver transplant. Genetic testingcould possibly be utilized to display relatives of the affected.
Wilson’s disease is a rare inherited disorder that causes copper to accumulate in your liver, brain and other vital organs. Most people with Wilson’s disease are diagnosed between the ages of 5 and 35, but it can affect younger and older people, as well.
Copper plays a key role in the development of healthy nerves, bones, collagen and the skin pigment melanin. Normally, copper is absorbed from your food, and excess is excreted through a substance produced in your liver (bile).
Symptoms of wilson’s disease
Wilson’s disease is present at birth, however, symptoms and signs do not appear till the copper accumulates in the brain, liver or other organ. Symptoms and signs vary depending upon the sections of the body affected by this illness. They could include:
- Golden-brown eye discoloration (Kayser-Fleischer rings)
- Fluid buildup in the legs or abdomen
- Problems with speech, swallowing or physical coordination
- Uncontrolled movements or muscle stiffness
- Fatigue, lack of appetite or abdominal pain
- A yellowing of the skin and the whites of the eye (jaundice)
Causes of wilson’s disease
Wilson’s disorder is inherited as an autosomal recessive trait, meaning it to develop the disorder you need to inherit 1 copy of the faulty gene from each parent. If you get just one abnormal gene, you will not be sick, but you are a carrier and may pass the gene to your children.




